I-type aluminum is a commonly used aluminum alloy profile in shipbuilding, and its cross-sectional shape is similar to the character "工".
The aluminum alloys commonly used in marine I-type aluminum are mainly 5xxx series and 6xxx series, such as 5083 aluminum alloy, 5086 aluminum alloy, 5456 aluminum alloy, 5383 aluminum alloy, 6061 aluminum alloy, 6063 aluminum alloy, etc. It is widely used due to its light weight, corrosion resistance and high strength, and is particularly suitable for hull structural parts with high requirements for strength and durability.

Marine aluminum alloys
5083 aluminum alloy: One of the most commonly used marine aluminum alloys, with excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, used in important parts such as hulls and decks.
5086 aluminum alloy: Similar to 5083 aluminum alloy, it has strong corrosion resistance, good welding performance, and excellent strength and toughness. It is used in structural parts such as hulls, keels, ribs, and brackets.
5456 aluminum alloy: higher strength than 5083, 5086 alloy, suitable for high-load main deck, frame and large hull structure.
6061 aluminum alloy: with good weldability and machining performance, mainly used for marine structural parts, pipelines and other load-bearing parts.
6063 aluminum alloy: excellent extrusion performance, good surface quality, suitable for complex profiles. Widely used in ship decorative parts, ship ladders, guardrails, etc.
5383 aluminum alloy: better corrosion resistance and weldability than 5083 aluminum alloy, high strength after welding. Suitable for ship welding structures, such as keels, ribs and large structural parts.
Specification
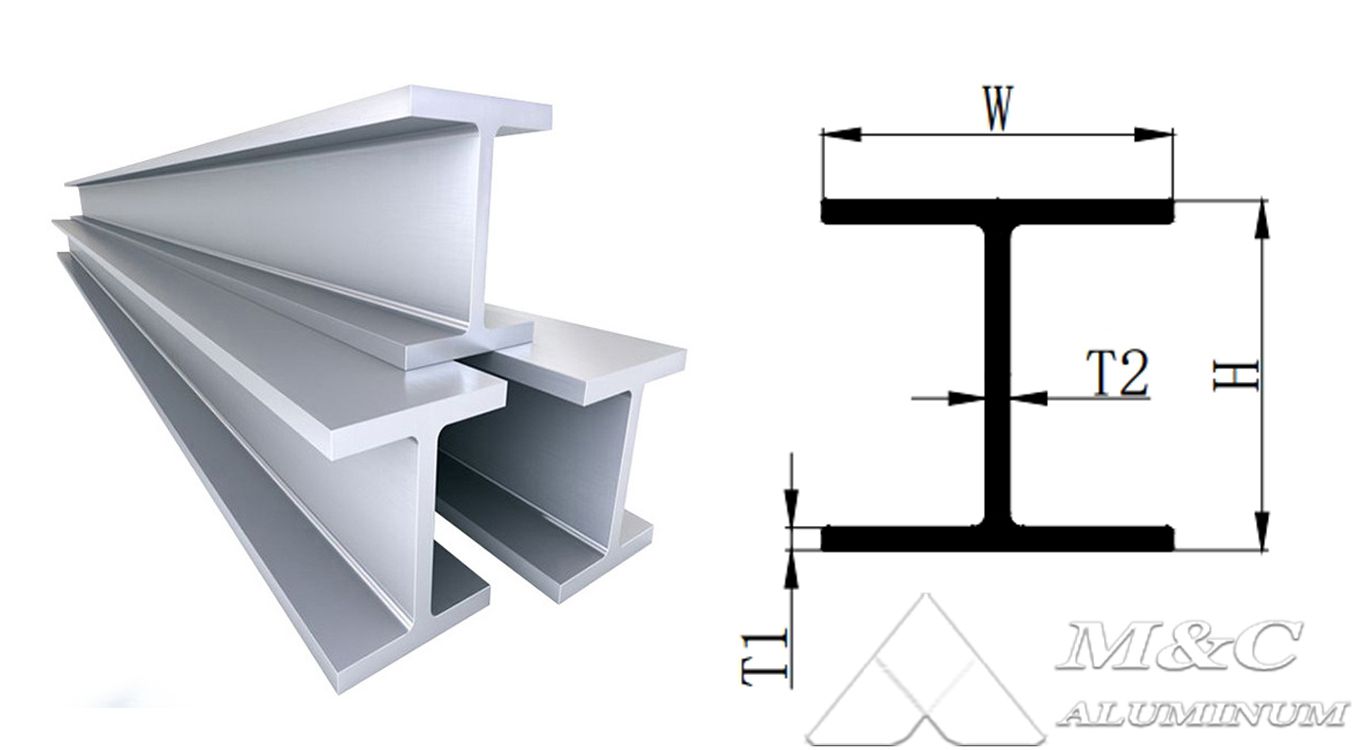
I-type aluminum specification parameters:
| I-type aluminum | |||
| H (mm) | W (mm) | T1 (mm) | T2 (mm) |
| 125 | 125 | 8 | 8 |
| 80 | 130 | 6 | 5 |
| 80 | 176 | 8 | 5 |
| 100 | 270 | 10 | 6 |
| 100 | 270 | 8 | 8 |
| 76.2 | 101.6 | 7.9 | 6.4 |
| 50 | 110 | 10 | 4 |
| 80 | 140 | 6 | 4 |
| 100 | 200 | 7 | 7 |
| 74 | 126 | 5 | 5 |
Marine I-types come in a variety of specifications, including different widths, heights, and wall thicknesses. When choosing marine I-types, you need to determine the appropriate specifications and models based on the specific use environment and requirements.
| Marine Aluminum I-type Aluminum Alloys Composition | |||||||||||||
| Alloy | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Ni | Zn | Ti | Ga | Other | Al | |
| Each | Total | ||||||||||||
| 5083 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.1 | 0.4-1.0 | 40.-4.9 | 0.05-0.25 | - | 0.25 | 0.15 | - | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |
| 5383 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.7-1.0 | 4.0-5.2 | 0.25 | - | 0.40 | 0.15 | - | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |
| 5086 | 0.40 | 0.50 | 0.1 | 0.2-0.7 | 3.5-4.5 | 0.05-0.25 | - | 0.25 | 0.15 | - | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |
| 5059 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.6-1.2 | 5.0-6.0 | 0.25 | - | 0.4-0.9 | 0.20 | - | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |
| 6061 | 0.4-0.8 | 0.7 | 0.15-0.4 | 0.15 | 0.8-1.2 | 0.04-0.35 | - | 0.25 | 0.15 | - | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |
| 6005A | 0.5-0.9 | 0.35 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.4-0.7 | 0.3 | - | 0.2 | 0.1 | - | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |
| 6082 | 0.7-1.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.4-1.0 | 0.6-1.2 | 0.25 | - | 0.2 | 0.1 | - | 0.05 | 0.15 | Remainder |
| Mechanical Properties of Marine Aluminum I-type | |||||||
Alloy | Form | Thickness(mm) | Temper | Rm | Rp0.2 | A% Min | |
Min. | Aso | Aso | |||||
5086 | Shapes, Bar, Tube | 3≤t≤50 | H112 | 240 | 95 | 10 | 12 |
| 5083 | Shapes, Bar, Tube Shapes, Bar, Tube | 3≤t≤50 | H111 | 270 270 | 110 125 | 10 10 | 12 12 |
| 5059 | Shapes, Bar, Tube | 3≤t≤50 | H112 | 330 | 200 | 10 | |
5383 | Shapes, Bar, Tub | 3≤t≤50 | O | 290 | 145 | 17 | 17 |
Shapes, Bar, Tub | 3≤t≤50 | H112 | 310 | 190 | 13 | ||
6061 | Shapes, Bar, Tube Profiles | 3≤t≤50 3≤t≤50 | T5 or T6 | 260 245 | 240 205 | 10 | 8 4 |
| 6005A | Shapes, Bar, Tube Profiles | 3≤t≤50 | T5 | 260 | 215 | 9 | 8 |
Shapes, Bar, Tube Profiles | 3≤t≤10 | T6 | 260 | 215 | 8 | 6 | |
3≤t≤10 | 250 | 200 | 8 | 6 | |||
6082 | Shapes, Bar, Tube Closed shapes | 3≤t≤50 3≤t≤50 | T5 or T6 | 310 290 | 260 240 | 10 | 8 5 |
Advantages
Features of I-type aluminum for ships:
1. Lightweight: The density of aluminum alloy is one-third of that of steel, which reduces the weight of the hull, increases speed and load, reduces fuel consumption, and improves economic benefits.
2. Strong corrosion resistance: Excellent performance in marine environment, resists seawater corrosion, extends the service life of the hull, and reduces maintenance costs.
3. Combination of strength and toughness: High strength, good ductility and impact resistance, suitable for applications under harsh marine conditions.
4. Easy processing: It can be welded, cut, formed and other processing methods, easy to manufacture complex structures, and reduce production costs.
Application
Application of I-type aluminum:
The "I"-shaped cross-section has excellent bending and shear resistance and can withstand greater pressure and impact. Therefore, it is widely used in the following fields in ship structures:
Keel: used to strengthen the hull structure and improve the overall rigidity of the hull.
Ship bracket: Supports the deck and bulkhead, lightweight and high strength to reduce the weight of the ship.
Frame and beam: widely used in ship frame and beam structures to help disperse stress and ensure hull stability.